In the rapidly evolving landscape of molecular biology, where speed and accuracy are paramount, traditional nucleic acid extraction methods often struggle to keep up in high-throughput settings. Enter magnetic bead-based extraction—a technique that combines efficiency with exceptional adaptability to automation. This post explores how magnetic bead-based extraction is reshaping the world of nucleic acid purification.
The Science Behind the Magnet
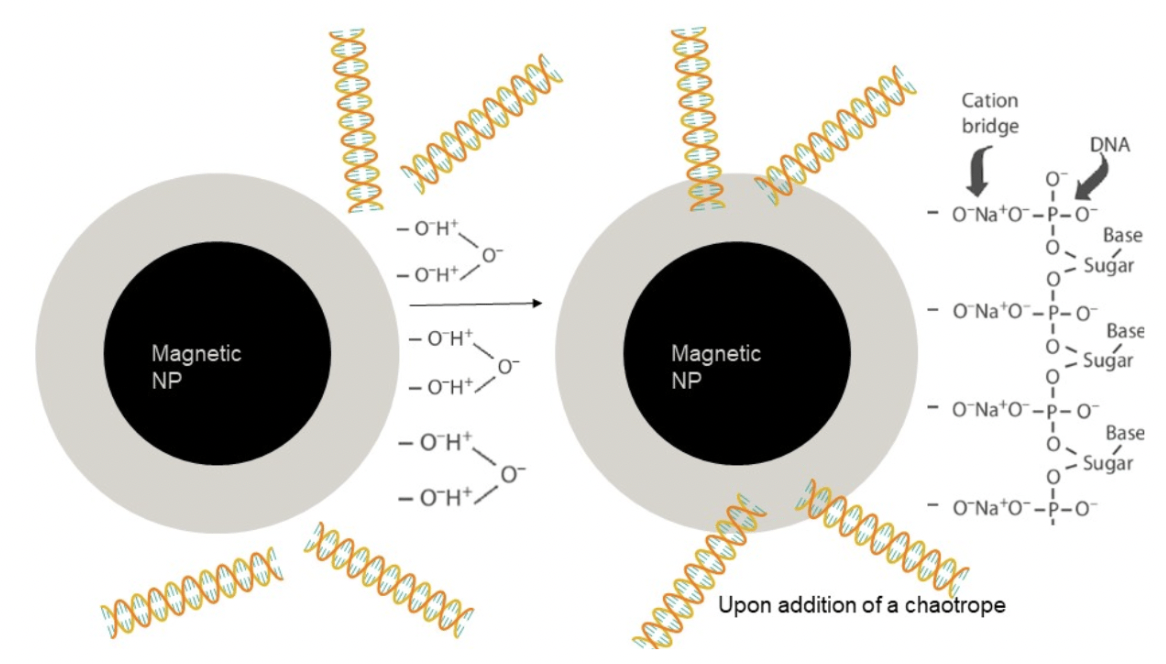
Central to this technique are microscopic magnetic beads coated with agents that bind selectively to nucleic acids. When a sample is mixed with these beads, DNA or RNA molecules adhere to them. Applying a magnet then separates the bead-bound nucleic acids from the rest of the sample, facilitating their purification.
Why Magnetic Beads?
- Speed and Simplicity: This method streamlines nucleic acid extraction by eliminating many steps required in traditional methods such as phenol-chloroform extraction or spin-columns, offering quicker results and often purer samples.
- Scalability: It can easily adjust to handle small or large sample volumes, making it ideal for varying research demands.
- Compatibility: Tailored to bind specifically to DNA, RNA, or particular nucleic acid sequences, these beads suit a wide range of applications.
- Reduced Waste: The process does not rely on columns or harsh chemicals, making it more environmentally friendly.
Automate to Dominate
Magnetic bead-based extraction excels when integrated with automation platforms:
- Consistency: Automated processes ensure uniform handling of all samples, reducing variability and enhancing reliability.
- Volume: Capable of processing hundreds of samples simultaneously, this method supports large-scale projects or busy diagnostic labs.
- Reduced Human Error: Automation minimizes manual handling, cutting down on cross-contamination and procedural mistakes.
- Efficiency: Systems operate with minimal oversight, freeing researchers to focus on data analysis or other tasks.
Application Horizons
Magnetic bead-based extraction’s versatility extends beyond research labs, including:
- Diagnostics: Quick nucleic acid extraction for PCR-based disease diagnostics.
- Genomics: Supporting large-scale genotyping or sequencing endeavors.
- Forensics: Facilitating DNA profiling from crime scene evidence.
- Agriculture: Enhancing crop breeding through rapid genotyping.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its advantages, magnetic bead-based extraction faces some challenges:
- Initial Investment: High-quality automation platforms require substantial upfront costs.
- Protocol Optimization: Some samples may need specific protocol adjustments to optimize yield.
- Bead Quality: The success of the extraction depends significantly on the quality of the magnetic beads used, necessitating reliable suppliers.
Conclusion
Magnetic bead-based extraction has significantly transformed nucleic acid purification. As molecular biology progresses towards more automated, high-throughput techniques, embracing such innovations will be crucial for advancing discovery and diagnostics.
Are you intrigued by the magnetic marvels of molecular biology? Subscribe for more insights and stay tuned to the latest developments in biotechnology.